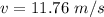Complete Question
The diagram for this question is showed on the first uploaded image (reference homework solutions )
Answer:
The velocity at the bottom is
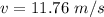
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The total distance traveled is
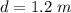
The mass of the block is
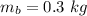
The height of the block from the ground is h = 0.60 m
According the law of energy
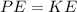
Where PE is the potential energy which is mathematically represented as
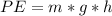
substituting values
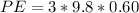
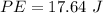
So
KE is the kinetic energy at the bottom which is mathematically represented as
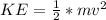
So
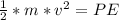
substituting values
=>
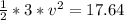
=>
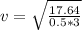
=>