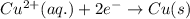Answer: The reaction that occurs at anode is
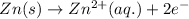
Step-by-step explanation:
Given :
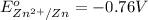
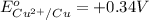
The substance having highest positive reduction potential will always get reduced and will undergo reduction reaction. Here, copper will undergo reduction reaction will get reduced.
The substance having highest negative reduction potential will always get oxidised and will undergo oxidation reaction. Here, zinc will undergo oxidation reaction will get oxidised.
Oxidation reaction occurs at anode and reduction reaction occurs at cathode.
Oxidation half reaction (anode) :
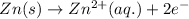
Reduction half reaction (cathode) :