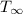Answer:
a) What is the surface temperature, in °C, after 400 s?
T (0,400 sec) = 800°C
b) Yes, the surface temperature is greater than the ignition temperature of oak (400°C) after 400 s
c) What is the temperature, in °C, 1 mm from the surface after 400 s?
T (1 mm, 400 sec) = 798.35°C
Step-by-step explanation:
oak initial Temperature = 25°C = 298 K
oak exposed to gas of temp = 800°C = 1073 K
h = 20 W/m².K
From the book, Oak properties are e=545kg/m³ k=0.19w/m.k Cp=2385J/kg.k
Assume: Volume = 1 m³, and from energy balance the heat transfer is an unsteady state.
From energy balance:
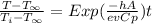
Initial temperature wall =
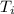
Surface temperature = T
Gas exposed temperature =