Answer:
Pressure exerted by the gas is 574.85 torr
Step-by-step explanation:
Atmospheric pressure = 751 torr
but 1 torr = 1 mmHg
therefore,
atmospheric pressure = 751 mmHg
1 mmHg = 133.3 Pa
therefore,
atmospheric pressure = 751 x 133.3 = 100108.3 Pa
distance labeled (tube section with mercury) = 176 mm
the pressure within the tube will be
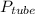 = ρgh
= ρgh
where ρ is the density of mercury = 13600 kg/m^3
h is the labeled distance = 176 mm = 0.176 m
g is acceleration due to gravity = 9.81 m/s^2
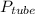 = 13600 x 9.81 x 0.176 = 23481.216 Pa
= 13600 x 9.81 x 0.176 = 23481.216 Pa
The general equation for the pressure in the manometer will be
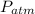 =
=
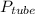 +
+
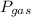
where
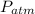 is the atmospheric pressure
is the atmospheric pressure
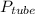 is the pressure within the tube with mercury
is the pressure within the tube with mercury
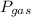 is the pressure of the gas
is the pressure of the gas
substituting, we have
100108.3 = 23481.216 +
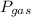
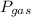 = 100108.3 - 23481.216 = 76627.1 Pa
= 100108.3 - 23481.216 = 76627.1 Pa
This pressure can be stated in mmHg as
76627.1 /133.3 = 574.85 mmHg
and also equal to 574.85 torr