Answer:
The horizontal acceleration of the block is 4.05 m/s².
Step-by-step explanation:
The horizontal acceleration can be found as follows:
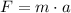
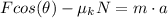
![Fcos(\theta) - \mu_(k)[mg - Fsen(\theta)] = m\cdot a](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/p0nianrazmfanq4dovc0wp7ifrm42s9jwq.png)
![a = (Fcos(\theta) - \mu_(k)[mg - Fsen(\theta)])/(m)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/y6kladpsi96i63yzc2h1lkdtreyjlmwfxe.png)
Where:
a: is the acceleration
F: is the force exerted by the rope = 28.2 N
θ: is the angle = 30°
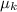 : is the kinetic coefficient = 0.12
: is the kinetic coefficient = 0.12
m: is the mass = 5 kg
g: is the gravity = 9.81 m/s²
![a = (28.2 N*cos(30) - 0.12[5 kg*9.81 m/s^(2) - 28.2 N*sen(30)])/(5 kg) = 4.05 m/s^(2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/siz9hbrisds5f0wcj0xhep50d2l124d35r.png)
Therefore, the horizontal acceleration of the block is 4.05 m/s².
I hope it helps you!