Answer:
A 95% confidence interval for the proportion of students who eat cauliflower on Jane's campus is [0.012, 0.270].
Explanation:
We are given that Jane wants to estimate the proportion of students on her campus who eat cauliflower. After surveying 24 students, she finds 2 who eat cauliflower.
Firstly, the pivotal quantity for finding the confidence interval for the population proportion is given by;
P.Q. =
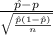 ~ N(0,1)
~ N(0,1)
where,
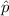 = sample proportion of students who eat cauliflower
= sample proportion of students who eat cauliflower
n = sample of students
p = population proportion of students who eat cauliflower
Here for constructing a 95% confidence interval we have used a One-sample z-test for proportions.
So, 95% confidence interval for the population proportion, p is ;
P(-1.96 < N(0,1) < 1.96) = 0.95 {As the critical value of z at 2.5% level
of significance are -1.96 & 1.96}
P(-1.96 <
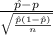 < 1.96) = 0.95
< 1.96) = 0.95
P(
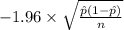 <
<
 <
<
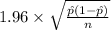 ) = 0.95
) = 0.95
P(
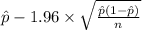 < p <
< p <
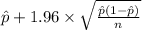 ) = 0.95
) = 0.95
Now, in Agresti and Coull's method; the sample size and the sample proportion is calculated as;
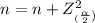
n =
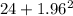 = 27.842
= 27.842
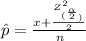 =
=
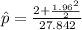 = 0.141
= 0.141
95% confidence interval for p = [
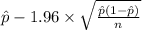 ,
,
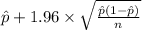 ]
]
= [
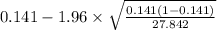 ,
,
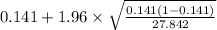 ]
]
= [0.012, 0.270]
Therefore, a 95% confidence interval for the proportion of students who eat cauliflower on Jane's campus [0.012, 0.270].
The interpretation of the above confidence interval is that we are 95% confident that the proportion of students who eat cauliflower on Jane's campus is between 0.012 and 0.270.