Answer:
Explanation:
Given that:
Mean μ= 100
standard deviation σ = 2.6
sample size n = 9
sample mean X = 100.6
The null hypothesis and the alternative hypothesis can be computed as follows:
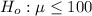
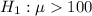
The numerical value for the test statistics is :
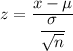
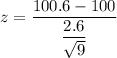
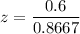
z = 0.6923
At ∝ = 0.05
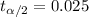
The critical value for the z score = 0.2443
From the z table, area under the curve, the corresponding value which is less than the significant level of 0.05 is 1.64
P- value = 0.244
c> If the true population mean is 101.3 ;
Then:
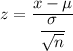
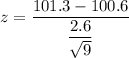
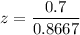
z = 0.808
From the normal z tables
P value = 0.2096