Answer:
The temperature order are;
(b) 96.62 K = (d) 96.62 K > (a) 48.31 K = (c) 48.31 K = (e) 48.31 K = (f) 48.31 K
Arrangement in order from highest to lowest and alphabetically gives;
(b) ↔ (d) → (a)↔ (c)↔ (e)↔ (f)
Explanation:
From the universal gas equation
P×V = N×k×T
Where:
P = Pressure
V = Volume
N = Number of molecules
k = Boltzmann constant = 1.38 × 10⁻²³ J/K
T = temperature
Therefore;
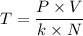
Which gives;
(a) When P = 100 kPa = 100,000 Pa, V = 4 L = 0.004 m³, N = 6 × 10²³, we have
100000*0.004/(6*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 48.31 K
(b) When P = 200 kPa = 200,000 Pa, V = 4 L = 0.004 m³, N = 6 × 10²³, we have
200000*0.004/(6*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 96.62 K
(c) When P = 50 kPa = 50,000 Pa, V = 8 L = 0.008 m³, N = 6 × 10²³, we have
50000*0.008/(6*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 48.31 K
(d) When P = 100 kPa = 100,000 Pa, V = 4 L = 0.004 m³, N = 3 × 10²³, we have
100000*0.004/(3*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 96.62 K
(e) When P = 100 kPa = 100,000 Pa, V = 2 L = 0.002 m³, N = 3 × 10²³, we have
100000*0.002/(3*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 48.31 K
(f) When P = 50 kPa = 50,000 Pa, V = 4 L = 0.004 m³, N = 3 × 10²³, we have
50000*0.004/(3*10^(23)*1.38*10^(-23)) = 48.31 K