Answer:
a) The magnitude of the change in the ball's momentum is 1.1 kilogram-meters per second, b) The change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum is -0.055 kilogram-meters per second, c) D. The magnitude of the change in the ball's momentum.
Step-by-step explanation:
a) This phenomenon can be modelled by means of the Principle of Momentum Conservation and the Impact Theorem, whose vectorial form is:
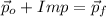
Where:
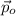 ,
,
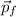 - Initial and final momentums, measured in kilogram-meters per second.
- Initial and final momentums, measured in kilogram-meters per second.
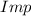 - Impact due to collision, measured in kilogram-meters per second.
- Impact due to collision, measured in kilogram-meters per second.
The impact experimented by the ball due to collision is:
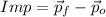
By using the definition of momentum, the expression is therefore expanded:
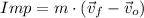
Where:
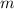 - Mass of the ball, measured in kilograms.
- Mass of the ball, measured in kilograms.
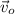 ,
,
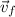 - Initial and final velocities, measured in meters per second.
- Initial and final velocities, measured in meters per second.
If
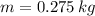 ,
,
![\vec v_(o) = -2.10\,j\,\left [(m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/nugatsvmrnlsciohbcc275bx5c0yjnux19.png) and
and
![\vec v_(f) = 1.90\,j\,\left [(m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/l8e28gtoxobrlfowdmt1n86bfskut9mceb.png) , the vectorial change of the linear momentum is:
, the vectorial change of the linear momentum is:
![Imp = (0.275\,kg)\cdot \left[1.90\,j+2.10\,j\right]\,\left[(m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/svr6hz80j8t1t6298rjzlt9n3nbdgy5wtc.png)
![Imp = 1.1\,j\,\left[(kg\cdot m)/(s) \right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/physics/college/xq7ey48meoedz4r7nk0ybqiffrfbakxn7a.png)
The magnitude of the change in the ball's momentum is 1.1 kilogram-meters per second.
b) The magnitudes of initial and final momentums of the ball are, respectively:
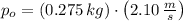
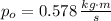
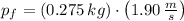
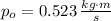
The change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum is:
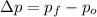
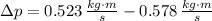
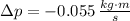
The change in the magnitude of the ball's momentum is -0.055 kilogram-meters per second.
c) The quantity calculated in part a) is more related to the net force acting on the ball during its collision with the floor, since impact is the product of net force, a vector, and time, a scalar, and net force is the product of the ball's mass and net acceleration, which creates a change on velocity.
In a nutshell, the right choice is option D.