Answer:
The minimum surface area of the container is 276.791 square units.
Explanation:
Let be
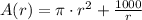 ,
,
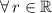 ,
,
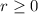 . The first and second derivatives of such function are, respectively:
. The first and second derivatives of such function are, respectively:
First derivative
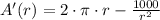
Second derivative
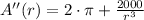
The critical values of
 are determined by equalizing first derivative to zero and solving it: (First Derivative Test)
are determined by equalizing first derivative to zero and solving it: (First Derivative Test)
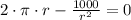
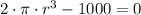
![r = \sqrt[3]{(1000)/(2\pi) }](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/dvdso0rs56jm0ogvvvd4pnt3zphs99d3aw.png)
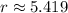 (since radius is a positive variable)
(since radius is a positive variable)
To determine if critical value leads to an absolute minimum, this input must be checked in the second derivative expression: (
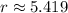 )
)
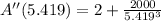
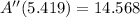
The critical value leads to an absolute minimum, since value of the second derivative is positive.
Finally, the minimum surface area of the container is:
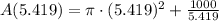
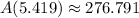
The minimum surface area of the container is 276.791 square units.