Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The pressure is
![[O_2] = 4.8 *10^(-5) \ atm](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5chmeij740c0sxs3d0kwfxmfq8pc7iplhd.png)
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The pressure of
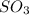 is
is
![[SO_3 ] = 0.63 \ atm](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6upxrlv9bujbqjehwm3zcyr05af8418c3n.png)
The pressure of
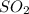 is
is
![[SO_ 2] = 0.30 \ atm](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/tquxa7s55a1lrt8c4tpvzhkmnadzvsvcnv.png)
The equilibrium constant is
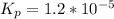
The reaction is
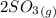 ⇔
⇔
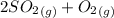
Generally the equilibrium constant is mathematically represented as
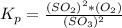
=>
![[O_2] = (k_p * [SO_3] ^2 )/([SO_2]^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/qpocyxi5ro41cw5baha9mxz4l89iu5qegc.png)
substituting values
![[O_2] = (1.2 *10^(-5) * 0.60 ^2 )/(0.30^2)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/kxxqn557faqe5kwmimvlytuojej6e71a23.png)
![[O_2] = 4.8 *10^(-5) \ atm](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/5chmeij740c0sxs3d0kwfxmfq8pc7iplhd.png)