Answer:
the smaller particle moves with speed of 8.706 m/s in the opposite direction to the bigger particle.
Step-by-step explanation:
Speed of the original particle = 13 m/s
We designate particles as A and B
The final weights of the component particles are
Particle A = 1.4 N
particle B = 1.9 N
The speed of the larger piece (particle B) = 29 m/s
We know that weight is the product of a body's mass and acceleration due to gravity g which is equal to 9.81 m/s^2, therefore, masses of the particles are
particle A = 1.4/9.81 = 0.143 kg
Particle B = 1.9/9.81 = 0.194 kg
The momentum of a body is the product of its mass and its velocity i.e
P = mv
This means that the mass of the particle before splitting is
0.143 kg + 0.194 kg = 0.337 kg
Momentum of the initial whole particle = mv
==> 0.337 x 13 = 4.381 kg-m/s
The bigger particle B remains horizontal, and has a momentum of
mv = 0.194 x 29 = 5.626 kg-m/s
According to the conservation of momentum, the total initial momentum of a system must be equal tot the total final momentum of the system.
Initial total momentum of the system = 4.381 kg-m/s (momentum of original particle before splitting)
Final total momentum of the system = Total momentum of the particles after splitting = 5.626 kg-m/s + ( 0.143 kg x
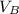 )
)
where
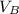 is the velocity of smaller particle A
is the velocity of smaller particle A
final total momentum of the system = 5.626 + 0.143
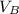
Equating the two momenta of the system, we'll have
4.381 = 5.626 + 0.143
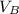
4.381 - 5.626 = 0.143
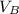
-1.245 = 0.143
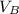
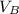 = -1.245/0.143 = -8.706 m/s
= -1.245/0.143 = -8.706 m/s
The negative sign indicates that the smaller particle moves in the opposite direction to the bigger particle