Answer:
1) a α, m I, W=F.d W =τ . θ,
2) a = v²/r
Step-by-step explanation:
1) The amounts of rotational and translational motion are related
acceleration is
a = d²x / dt²
linear displacement is equivalent to angular rotation, therefore angular acceleration is
α = d²θ / dt²
force in linear motion is equivalent to moment in endowment motion
F = m a
τ = I α
the mass is the inertia of the translation, in rotational motion the moment of inertia is the rotational inertia
I = m r²
Work is defined by W = F. d
in rotation it is defined by W = τ . θ
The linear momentum is p = mv
the angular momentum L = I w
momentum the linear motion is I = F dt
in the rotation it is I = τ dt
2) The velocity is a vector therefore it has modulus and direction, linear acceleration changes the modulus of velocity, whereas circular motion changes the direction (the other element of the vector).
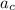 Ac = v²/r
Ac = v²/r