Answer:
The magnetic field is

Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The mass of the metal rod is

The current on the rod is

The distance of separation(equivalent to length of the rod ) is
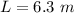
The coefficient of kinetic friction is

The kinetic frictional force is

The constant speed is

Generally the magnetic force on the rod is mathematically represented as
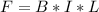
For the rod to move with a constant velocity the magnetic force must be equal to the kinetic frictional force so
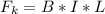
=>

=>

=>
