Answer:
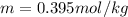
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
This is a problem about boiling point elevation which is modeled via:

Whereas for this solvent (nonpolar, nonionizing), the van't Hoff factor is one. In such a way, the molality of the solute is simply computed as shown below:
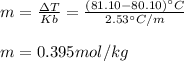
In this manner, we can also compute the molar mass of the solute by noticing 20.0 g (0.020 kg) of benzene were used:
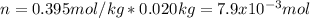
And considering the 2.15 g of the solute:
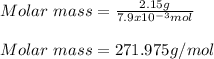
Best regards.