Answer:
a
The null hypothesis is
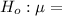 $98
$98
The alternative hypothesis is
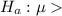 $98
$98
b
test statistics
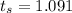
c
The the result of the test statistics is significant
Explanation:
From the question we are told that
The population mean is
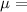 $98
$98
The standard deviation is
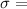 $11
$11
The sample size is

The sample mean is
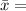 $100
$100
The level of significance is
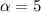 % = 0.05
% = 0.05
The null hypothesis is
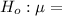 $98
$98
The alternative hypothesis is
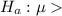 $98
$98
Now the critical values for this level of significance obtained from critical value for z-value table is
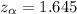
The test statistics is mathematically evaluated as
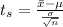
substituting values
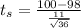
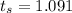
Looking at
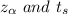 we see that
we see that
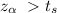 hence the we fail to reject the null hypothesis
hence the we fail to reject the null hypothesis
hence there is no sufficient evidence to conclude that the mean weekly food budget for all households in this community is higher than the national average.
Thus the the result is significant