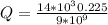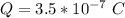Answer:
The excess charge is
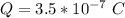
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The diameter is
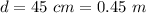
The potential of the surface is
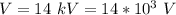
The radius of the sphere is
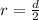
substituting values
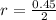
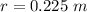
The potential on the surface is mathematically represented as
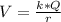
Where k is coulomb's constant with value
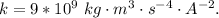
given from the question that there is no other charge the Q is the excess charge
Thus
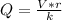
substituting values