Answer:
The drag coefficient of the car is 0.189
Step-by-step explanation:
mass of the car = 2250 kg
Frontal area of the car = 2.35 m^2
initial speed of the car = 72 km/hr = (72 x 1000)/3600 = 20 m/s
final speed of the car = 54 km/hr = (54 x 1000)/3600 = 15 m/s
time taken by the car to slow down = 105 sec
We'll assume that the value of the drag coefficient is constant throughout the deceleration.
The car decelerates from 20 m/s to 15 m/s in 105 seconds, the deceleration is calculated from
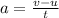
where a is the deceleration
v is the final speed of the car
u is the initial speed of the car
t is the time taken to decelerate.
imputing values, we'll have
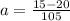 = -0.0476 m/s^2 (the -ve sign indicates a deceleration, which is a negative acceleration)
= -0.0476 m/s^2 (the -ve sign indicates a deceleration, which is a negative acceleration)
we can safely ignore the -ve sign in other calculations that follows
The force (drag force) with which the air around the decelerates the car is equal to..
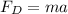
where
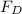 is the drag force
is the drag force
m is the mass of the car
a is the deceleration of the car
imputing values, we'll have
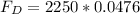 = 107.1 N
= 107.1 N
equation for drag force is
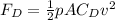
where p is the air density ≅ 1.225 kg/m³
A is the frontal area of the car
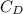 is drag coefficient of the car
is drag coefficient of the car
v is the relative velocity of air and the car, and will be taken as the initial velocity of the car before starting to decelerate.
imputing these values, we'll have
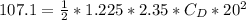 = 575.75
= 575.75
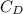
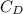 = 107.1/575.75 = 0.189
= 107.1/575.75 = 0.189