Answer:
2-ethoxy-2-methylpropan-1-ol
Step-by-step explanation:
On this reaction, we have an "epoxide" (2-methyl-1,2-epoxypropane). Additionally, we have acid medium (due to the sulfuric acid
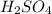 ). The acid medium will produce the hydronium ion (
). The acid medium will produce the hydronium ion (
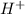 ). This ion would be attacked by the oxygen of the epoxide. Then a carbocation would be produced, in this case, the most stable carbocation is the tertiary one. Then an ethanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and will attack the carbocation. Finally, a deprotonation step takes place to produce 2-ethoxy-2-methylpropan-1-ol.
). This ion would be attacked by the oxygen of the epoxide. Then a carbocation would be produced, in this case, the most stable carbocation is the tertiary one. Then an ethanol molecule acts as a nucleophile and will attack the carbocation. Finally, a deprotonation step takes place to produce 2-ethoxy-2-methylpropan-1-ol.
See figure 1
I hope it helps!