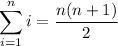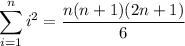Split up the interval [0, 8] into 4 equally spaced subintervals:
[0, 2], [2, 4], [4, 6], [6, 8]
Take the right endpoints, which form the arithmetic sequence
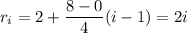
where 1 ≤ i ≤ 4.
Find the values of the function at these endpoints:
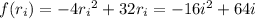
The area is given approximately by the Riemann sum,
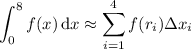
where
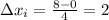 ; so the area is approximately
; so the area is approximately
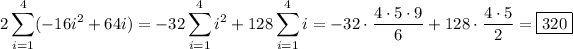
where we use the formulas,