Answer and Step-by-step explanation: P(X) calculated by the binomial probability formula is:
P(X) =
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}n\\X\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/o838r0ocj47clhx4wh9zcgudrcdrmunjyi.png) .
.
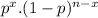
P(20) =
![\left[\begin{array}{ccc}53\\20\end{array}\right] .(0.3)^(20).(1-0.3)^(33)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/a095boirwi9opy9c5cw6w4gqotcgo71gml.png)
P(20) =
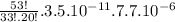
P(20) = 0.0552
To determine whether the normal distribution can be used to estimate this probability, both n.p and n.(1-p) must be greater than 5:
n . p = 53*0.3 = 15.9
n.(1-p) = 53(1-0.3) = 37.1
Since both ARE greater than 5, normal distribution can be used.
To approximate:
mean = n . p = 15.9
standard deviation =
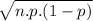 = 3.34
= 3.34
Find the z-score:
z =
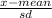 =
=
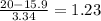
z-score = 0.8907
Comparing values:
0.8907 - 0.0552 = 0.8355