Answer:
The number of moles of X2(g) present at equilibrium is 0.0981.
Step-by-step explanation:
Being:
aA + bB ⇔ cC + dD
the reaction constant Kc is defined as:
![Kc=([C]^(c) *[D]^(d) )/([A]^(a)*[B]^(b) )](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/mj1hrqvs04jazeulfuhi036fhkedztq05x.png)
That is, the constant Kc is equal to the multiplication of the concentrations of the products raised to their stoichiometric coefficients by the multiplication of the concentrations of the reactants also raised to their stoichiometric coefficients.
Being the balanced reaction:
H₂(g) + X₂(g) ⇔ 2 HX (g)
the constant Kc is:
![Kc=([HX]^(2) )/([H_(2) ]*[X_(2) ])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/s4ee79rlb110jp519a5ptrhv1e17vanxhg.png)
In this case, Kc = 24.4 and being
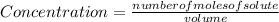 :
:
Replacing in the definition of the constant of Kc:
![24.4=(0.2^(2) )/(0.05*[X_(2) ])](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hqn5zmb76a6hq0aqlv1f1tl49ww49yhfsa.png)
Solving:
![[X_(2) ]=(0.2^(2) )/(0.05*24.4)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/wznvgbetxw8gw5qni1nzv5nupx2hk2zttv.png)
[X₂]= 0.0327
Applying the definition of concentration
![[X_(2) ]=(number of moles of X_(2) )/(volume)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/ehjgq6nv1jv8l7w2l932ot7x6jr8s9xyy6.png) , and the volume being 3 liters:
, and the volume being 3 liters:
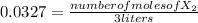
Solving:
number of moles of X₂= 0.0327* 3 liters
number of moles of X₂= 0.0981
The number of moles of X2(g) present at equilibrium is 0.0981.