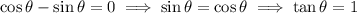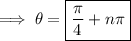I suppose the curve is
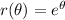 .
.
Tangent lines to the curve have slope
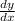 ; use the chain rule to get this in polar coordinates.
; use the chain rule to get this in polar coordinates.
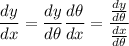
We have
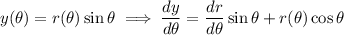
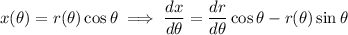
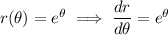
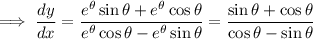
The tangent line is horizontal when the slope is 0, which happens wherever the numerator vanishes:
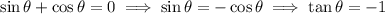
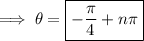
(where
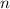 is any integer)
is any integer)
The tangent line is vertical when the slope is infinite or undefined, which happens when the denominator is 0: