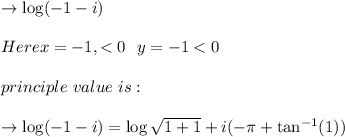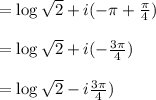Answer:
Following are the answer to this question:
Explanation:
The principle vale of Arg(3)
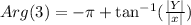
The principle value of the
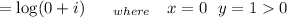
So, the principle value:
a)
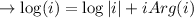
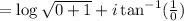
b)
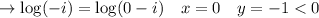
Principle value:
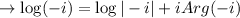
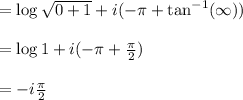
c)
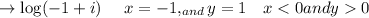
The principle value:

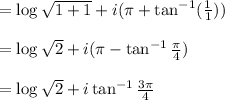
d)
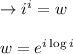
The principle value:
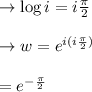
e)
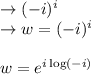
In this we calculate the principle value from b:
so, the final value is
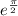
f)
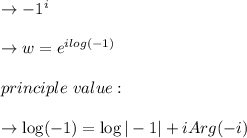
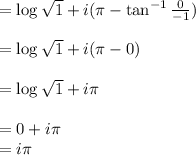
and the principle value of w is =
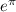
g)
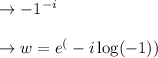
from the point f the principle value is:
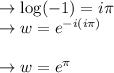
h)