Answer:
b. 0.585
Explanation:
According to Bayes' theorem:
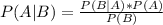
Let A = Person is infected, and B = Person tested positive. Then:
P(B|A) = 93.9%
P(A) = 5.8%
P(B) = P(infected and positive) + P(not infected and positive)
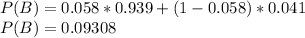
Therefore, the probability that a person has the disease given that the test result is positive, P(A|B), is:
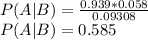
The probability is 0.585.