Answer:
i. 6.923 V
ii. The e.m.f. = 22.5 V
Step-by-step explanation:
i. The given parameters are;
Length of potentiometer = 1 m
The resistance of the potentiometer = 10 Ω
The e. m. f. of the attached cell = 9 V
The current, I flowing in the circuit = e. m. f/(Total resistance)
The current, I flowing in the circuit = 9 V/(10 + 3) = 9/13 A
The potential difference, p.d. across the 1 m potentiometer wire = I × Resistance of the potentiometer wire
The p.d. across the potentiometer wire = 9/13×10 = 90/13 = 6.923 V
ii) Given that the 1 m potentiometer wire has a resistance of 10 Ω, 75 cm which is 0.75 m will have an e.m.f. given by the following relation;
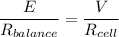
Where:
E = e.m.f. of the balance point cell
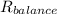 = Resistance of 75 cm of potentiometer wire = 0.75×10 = 7.5 Ω
= Resistance of 75 cm of potentiometer wire = 0.75×10 = 7.5 Ω
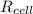 = Resistance of the cell in the circuit = 3 Ω
= Resistance of the cell in the circuit = 3 Ω
V = e.m.f. attached cell = 9 V
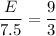
E = 7.5*3 = 22.5 V
The e.m.f. = 22.5 V