Nitrogen gas is the limiting reactant.
To determine the limiting reactant, we first need to write the balanced chemical equation for the reaction between nitrogen gas and hydrogen gas to produce ammonia. The balanced equation is:
![\[ N_2(g) + 3H_2(g) \rightarrow 2NH_3(g) \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/2xbc2og8jmmbam7j5tjoi7qlxhs3e9p19n.png)
Now, let's use the given masses to calculate the moles of each reactant:
Moles of
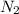 :
:
![\[ \text{Moles} = \frac{\text{Mass}}{\text{Molar Mass}} = \frac{23.2 \, \text{g}}{28.02 \, \text{g/mol}} \approx 0.826 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/9vk3awexaljn4bfmmk3rcep7c7sntfdsph.png)
Moles of \(H_2\):
![\[ \text{Moles} = \frac{\text{Mass}}{\text{Molar Mass}} = \frac{23.2 \, \text{g}}{2.016 \, \text{g/mol}} \approx 11.5 \, \text{mol} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/ikbmyhzfvfwa6hweiksk7ycnihco7b6u3t.png)
Now, using the coefficients from the balanced equation, we can determine the stoichiometric ratio of moles:
![\[ \frac{\text{Moles of } N_2}{1} = \frac{\text{Moles of } H_2}{3} \]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/fpc5ili952xojdrdnatu5ut2svbt66z7cx.png)
Since the actual ratio is
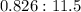 , which is less than
, which is less than
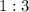 , nitrogen gas
, nitrogen gas
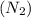 is the limiting reactant.
is the limiting reactant.