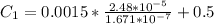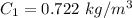Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The concentration of high-pressure side is
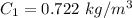
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The thickness of the polyethylene is
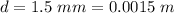
The temperature is
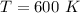
The flux is
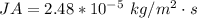
The concentration on the low-pressure side is
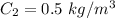
The initial diffusivity is
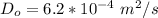
The activation energy for diffusion is
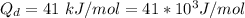
Generally the diffusivity of the oxygen at 600 K can be mathematically evaluated as
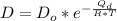
substituting values
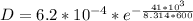

Generally the flux is mathematically represented as
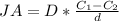
Where
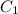 is the concentration of oxygen at the higher side
is the concentration of oxygen at the higher side
So
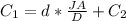
substituting values