Answer:
(a) Increasing:
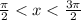 and Decreasing:
and Decreasing:
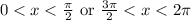
(b) The local minimum and maximum values are -16 and 16 respectively.
(c) The inflection points are
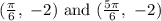
Explanation:
The function provided is:
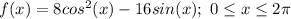
(a)
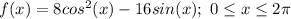
Then,
![f'(x)=-16cos(x)sin(x)-16cos(x)=-16cos(x)[1+sin(x)]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/ys753hoczs53sitq48r9ci2hp42bo36hzl.png)
Note,
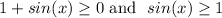
Then,
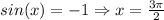 for
for
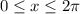 .
.
Also
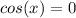 .
.
Thus, f (x) is increasing for,
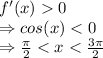
And f (x) is decreasing for,
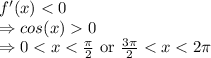
(b)
From part (a) f (x) changes from decreasing to increasing at
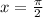 and from increasing to decreasing at
and from increasing to decreasing at
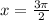 .
.
The local minimum value is:

The local maximum value is:
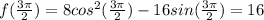
(c)
Compute the value of f'' (x) as follows:
![f''(x)=16sin(x)[1+sin(x)]-16cos^(2)(x)\\\\=16sin(x)+16sin^(2)(x)-16[1-sin^(2)(x)]\\\\=32sin^(2)(x)+16sin(x)-16\\\\=16[2sin(x)-1][sin (x)+1]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/3ij7yszbi3a2ec6pxoc0mpnstqnzqczi7e.png)
So,
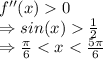
And,
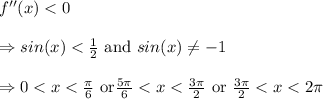
Thus, f (x) is concave upward on
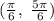 and concave downward on
and concave downward on
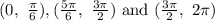 .
.
If
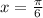 , then f (x) will be:
, then f (x) will be:
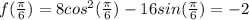
If
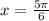 , then f (x) will be:
, then f (x) will be:
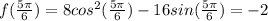
The inflection points are
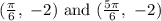 .
.