Answer:
The probability that the combined sample tests positive for the virus is 0.083
Since the probability that combined sample test positive for the virus is greater than 0.05, it is not likely for such a combined sample to test positive.
The probability that the combined sample will test positive is 0.083
Explanation:
Given that:
The probability of a randomly selected adult in one country being infected with a certain virus is 0.003.
P = 0.003
number of blood sample size n = 29
The probability mass function of X is as follows;
![P(X=x) = \left[\begin{array}{c}{29}&x\\\end{array}\right] (0.003)^x (1-0.003)^(29-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/m15wkxll11ef3pc7jvaybox8kjxh1qwayt.png)
Thus; the required probability is;
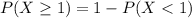
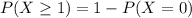
![P(X \geq 1) = 1 - \left[\begin{array}{c} (29!)/(0!(29-0)!) \ \ * 0.003)^0 * (1-0.003)^(29-0)}\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/pykevn2w7pmgvvjmtia3bmw1sylxocyv15.png)
![P(X \geq 1) = 1 - \left[\begin{array}{c} 1 * 1 * ( 0.9166)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/r7y50pxav0xok3nkru9i8ds74jukouqvda.png)
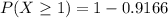
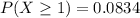
Therefore; the probability that the combined sample tests positive for the virus is 0.083
Is it unlikely for such a combined sample to test positive?
P(combined sample test positive for the virus ) = 0.0834
Since the probability that combined sample test positive for the virus is greater than 0.05, it is not likely for such a combined sample to test positive.
The probability of a randomly selected adult in one country being infected with a certain virus is 0.003.
P = 0.003
number of blood sample size n = 29
The probability mass function of X is as follows;
![P(X=x) = \left[\begin{array}{c}{29}&x\\\end{array}\right] (0.003)^x (1-0.003)^(29-x)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/m15wkxll11ef3pc7jvaybox8kjxh1qwayt.png)
Thus; the required probability is;
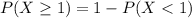
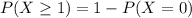
![P(X \geq 1) = 1 - \left[\begin{array}{c} (29!)/(0!(29-0)!) \ \ * 0.003)^0 * (1-0.003)^(29-0)}\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/pykevn2w7pmgvvjmtia3bmw1sylxocyv15.png)
![P(X \geq 1) = 1 - \left[\begin{array}{c} 1 * 1 * ( 0.9166)\end{array}\right]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/middle-school/r7y50pxav0xok3nkru9i8ds74jukouqvda.png)
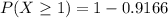
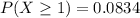
The probability that the combined sample will test positive is 0.083