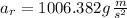Answer:
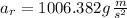
Step-by-step explanation:
Let suppose that centrifuge is rotating at constant angular speed, which means that resultant acceleration is equal to radial acceleration at given radius, whose formula is:
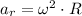
Where:
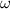 - Angular speed, measured in radians per second.
- Angular speed, measured in radians per second.
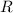 - Radius of rotation, measured in meters.
- Radius of rotation, measured in meters.
The angular speed is first determined:
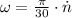
Where
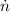 is the angular speed, measured in revolutions per minute.
is the angular speed, measured in revolutions per minute.
If
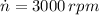 , the angular speed measured in radians per second is:
, the angular speed measured in radians per second is:
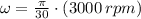
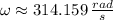
Now, if
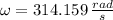 and
and
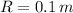 , the resultant acceleration is then:
, the resultant acceleration is then:
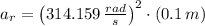
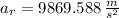
If gravitational acceleration is equal to 9.807 meters per square second, then the radial acceleration is equivalent to 1006.382 times the gravitational acceleration. That is: