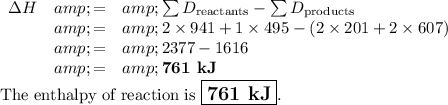Answer:
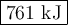
Step-by-step explanation:
You calculate the energy required to break all the bonds in the reactants.
Then you subtract the energy needed to break all the bonds in the products.
N₂ + O₂ ⟶ 2NO
N≡N + O=O ⟶ 2O-N=O
Bonds: 2N≡N 1O=O 2N-O + 2N=O
D/kJ·mol⁻¹: 941 495 201 607