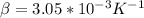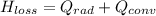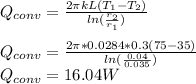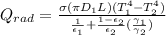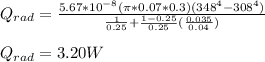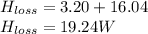Note: The diagram attached below is the completion of the given question.
Also calculate the heat loss from the coffee due to radiation and the total heat loss
Answer:
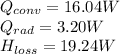
Step-by-step explanation:
Glass diameter of the coffee container,
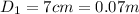
Glass radius of the coffee container, r₁ = 0.07/2 = 0.035 m
Diameter of the aluminium housing,
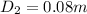
Radius of the aluminium housing, r₂ = 0.08/2 = 0.04 m
Inner temperature, T₁ = 75°C = 348 K
Outer temperature, T₂ = 35°C = 308 K
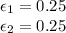
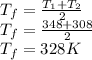
At
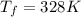 , P = 1 atm
, P = 1 atm
k = 0.0284 w/m-k, v = 23.74 * 10⁻⁶,
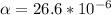 , pr = 0.703,
, pr = 0.703,