Answer:
The average angular acceleration is 0.05 radians per square second.
Step-by-step explanation:
Let suppose that Ferris wheel accelerates at constant rate, the angular acceleration as a function of change in angular position and the squared final and initial angular velocities can be clear from the following expression:
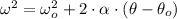
Where:
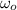 ,
,
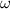 - Initial and final angular velocities, measured in radians per second.
- Initial and final angular velocities, measured in radians per second.
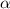 - Angular acceleration, measured in radians per square second.
- Angular acceleration, measured in radians per square second.
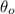 ,
,
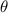 - Initial and final angular position, measured in radians.
- Initial and final angular position, measured in radians.
Then,
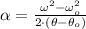
Given that
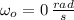 ,
,
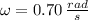 and
and
 , the angular acceleration is:
, the angular acceleration is:
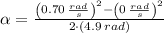
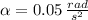
Now, the time needed to accelerate the Ferris wheel uniformly is described by this kinematic equation:
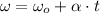
Where
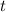 is the time measured in seconds.
is the time measured in seconds.
The time is cleared and obtain after replacing every value:
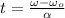
If
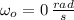 ,
,
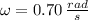 and
and
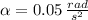 , the required time is:
, the required time is:
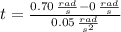
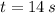
Average angular acceleration is obtained by dividing the difference between final and initial angular velocities by the time found in the previous step. That is:
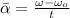
If
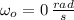 ,
,
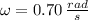 and
and
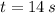 , the average angular acceleration is:
, the average angular acceleration is:
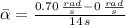
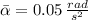
The average angular acceleration is 0.05 radians per square second.