Answer:
a)
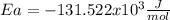
b)
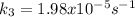
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
a) In this case, for this kinetics problem, we can consider the temperature-dependent Arrhenius equation:
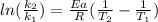
In such a way, for the given temperatures and rate constant, we compute the activation energy as follows:
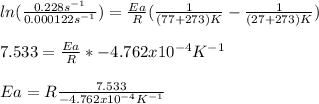
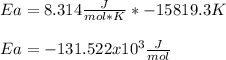
b) In this case, we use the previously computed activation energy in order to compute the rate constant at the asked 17°C:
![k_3=k_1exp((Ea)/(R)((1)/(T_2)-(1)/(T_1) ))\\\\k_3=0.000122s^(-1)exp[(-131.522x10^3(J)/(mol) )/(8.314(J)/(mol*K))*((1)/((17+273)K) -(1)/((27+273)K) )]\\\\k_3=1.98x10^(-5)s^(-1)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/r7x3rgw6ji02f8gyljuj2qzm04lkkz98cq.png)
Best regards.