Answer:
Effective resistance of two equal resistors in series is twice that of a single resistor and in essence will reduce the amount of current flowing in the circuit.
Step-by-step explanation:
When two resistors are connected in series, their effective resistance is the sum of their individual resistances. For example, given two resistors of resistance values R₁ and R₂, their effective resistance, Rₓ is given by;
Rₓ = R₁ + R₂ --------------(1)
If these resistors have equal resistance values, say R, then equation 1 becomes;
Rₓ = R + R
Rₓ = 2R
This means that their effective resistance is twice of their individual resistances. In other words, when two equal resistors are in series, their effective resistance is twice the resistance of each single one of those resistors.
Now, according to Ohm's law, voltage(V) is the product of current (I) and resistance (R). i.e
V = IR
I =
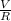
We can deduce that current increases as resistance decreases and vice-versa.
So, if the two equal resistors described above are connected in series, the amount of current flowing will be reduced compared to having just a single resistor.