Answer:
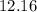
Step-by-step explanation:
We have to start with the reaction between nitric acid and potassium hydroxide:
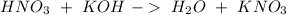
With this in mind, we can calculate the number of moles of each compound if we use the molarity equation:
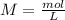 (this means that we have to find the Litters dividing by 1000)
(this means that we have to find the Litters dividing by 1000)
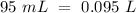
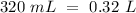
Now, we can calculate the moles:
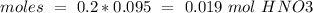
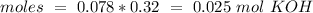
If we have a molar ratio 1:1 (1 mol of
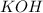 reacts with 1 mol of
reacts with 1 mol of
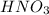 ). So, if we have
). So, if we have
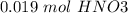 we will need
we will need
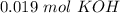 . So, we have to calculate the amount of KOH that remains in the solution, so:
. So, we have to calculate the amount of KOH that remains in the solution, so:
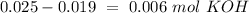
If we have an excess of KOH, this compound will be the cause of the pH value. Therefore we have to calculate the concentration. We already know the moles we have to calculate the volume. The total volume:
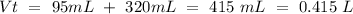
With this value, we can calculate the concentration of KOH:
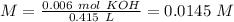
We have to keep in mind that this compound is a base, so we have to calculate the pOH value first and then the pH:
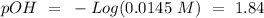
If we remember that: 14 = pH + pOH we can find the pH value:
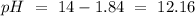
I hope it helps!