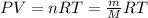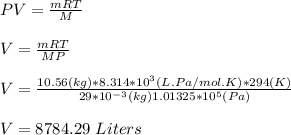Complete question:
(a) compute the specific heat capacity at constant volume of nitrogen gas. the molar mass of N₂ is 29.0 You warm 1.8 kg of water at a constant volume 1.00 L from 21 C to 30.5 C in a kettle. For the same amount of heat, how many kilograms of 21∘C air would you be able to warm to 30.5∘C ?
(b) What volume (in liters) would this air occupy at 21∘C and a pressure of 1.00 atm? Make the simplifying assumption that air is 100% N₂
Answer:
(a) The specific heat capacity of N₂ is 715.86 J/kg.K
(b) The volume the air occupy at 21∘C is 8784.29 Liters
Step-by-step explanation:
Given;
M is the molar mass of N₂ = 29 x 10⁻³ kg/mol
specific heat of N₂ at constant volume, Cv = 20.76 J/mol.K
(a)
The specific heat capacity of N₂ is calculated as;
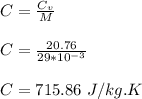
(b) heat capacity of water;
Q = mcΔθ
where;
c is the specific heat capacity of water = 4200 J/kg.K
m is mass of water, = 1.8 kg
Δθ is change in temperature, = 30.5 - 21 = 9.5 °C
Q = 1.8 x 4200 x 9.5
Q = 71820 J
Mass of nitrogen gas N₂, at this quantity of heat;
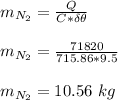
The volume this air occupy at 21∘C
Apply ideal gas law;