Answer:
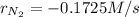
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, by means of the law of mass action, we firstly write the described chemical reaction:
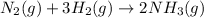
Thus, as ammonia is being formed at 0.345 M/s, nitrogen will be disappearing at (consider law of mass action):
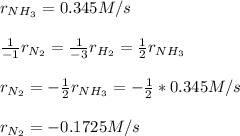
Best regards.