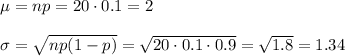Answer:
a) P(X ≤ 2) = 0.677
b) P(X ≥ 5) = 0.043
c) P(1 ≤ X ≤ 4) = 0.835
d) P(x=0) = 0.072
e) expected value: 2 boards
standard deviation: 1.34 boards
Explanation:
We can model this with a binomial random variable, with sample size n=20 and probability of success p=0.1.
The probability that k number of defective boards in the sample is:
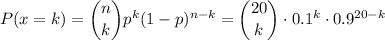
a) We have to calculate the probability that 2 or less number of defective boards. This can be calculated as:
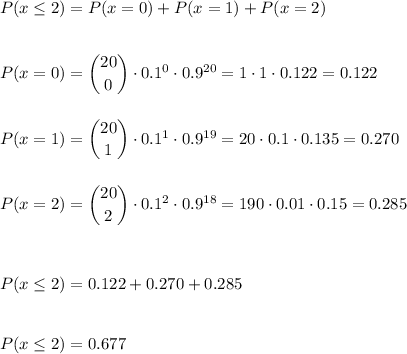
The probability that 2 or less number of defective boards is 0.677.
b) We have to calculate the probability that 5 or more number of defective boards. This can be calculated as:
![P(x\geq5)=1-[P(x=0)+P(x=1)+P(x=2)+P(x=3)+P(x=4)]\\\\\\P(x=0)=\dbinom{20}{0}\cdot0.1^(0)\cdot0.9^(20)=1\cdot1\cdot0.122=0.122\\\\\\P(x=1)=\dbinom{20}{1}\cdot0.1^(1)\cdot0.9^(19)=20\cdot0.1\cdot0.135=0.270\\\\\\P(x=2)=\dbinom{20}{2}\cdot0.1^(2)\cdot0.9^(18)=190\cdot0.01\cdot0.15=0.285\\\\\\P(x=3)=\dbinom{20}{3}\cdot0.1^(3)\cdot0.9^(17)=1140\cdot0.001\cdot0.167=0.190\\\\\\P(x=4)=\dbinom{20}{4}\cdot0.1^(4)\cdot0.9^(16)=4845\cdot0.0001\cdot0.185=0.090\\\\\\\\\\\\](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/yyicjnmlf4m7957u0lzzdxdk22rfj271dn.png)
![P(x\geq5)=1-[0.122+0.270+0.285+0.190+0.090]\\\\P(x\geq5)=1-0.957=0.043](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/mathematics/college/rz97odg3yqihpr79nn0ws839tc03fs55si.png)
The probability that 5 or more number of defective boards is 0.043.
c) We have to calculate P(1 ≤ X ≤ 4)
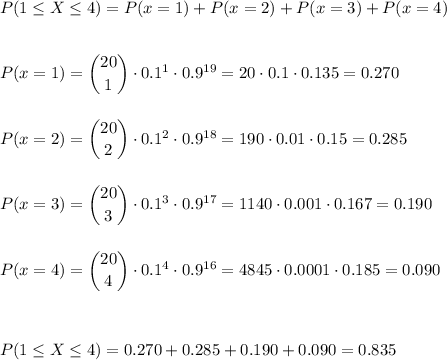
d) The probability that none of the 25 boards is defective is P(x=0), but now calculated for a sample size n=25.
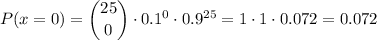
e) The expected value and standard deviation for X (n=20, p=0.1) are: