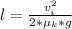Complete Question
The complete question is shown on the first uploaded image
Answer:
The distance which the car skid is
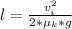
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The initial velocity of the car is
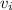
The coefficient of kinetic friction is
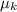
According to the law of energy conservation
The initial Mechanical Energy = The final Mechanical Energy
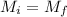
The initial mechanical energy is mathematically represented as

where KE is the initial kinetic energy which is mathematically represented as
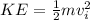
And PE is the initial potential energy which is zero given that the car is on the ground
Now
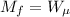
Where
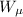 is the work which friction exerted on the car which is mathematically represented as
is the work which friction exerted on the car which is mathematically represented as
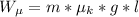
Where
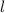 is the distance covered by the car before it slowed down
is the distance covered by the car before it slowed down
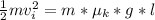
=>