Answer:
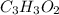
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, since the law of conservation of mass allows us to notice that the mass of carbon in the burned compound is also present in the resulting carbon dioxide, we can compute such moles as shown below:
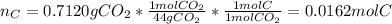
Next, hydrogen in the sample is present at the products in the water only, and in one mole of water, two moles of hydrogen are present, thereby:
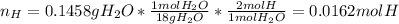
Nevertheless, the amount of oxygen in the sample must be computed by subtracting both the mass of carbon and hydrogen from the previously computed moles:
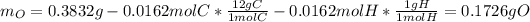
And the moles:
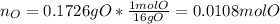
Next, we compute the mole ratios with respect to the element having the smallest number of moles (oxygen) to obtain the subscripts in the empirical formula:
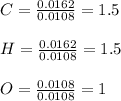
Then, we have:
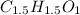
Finally, by multiplying by two, we obtain the smallest whole subscripts:
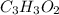
Best regards.