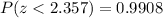Answer:
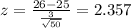
And we can find the probability using the normal distribution table and we got:
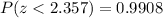
Explanation:
Let X the random variable of interest and we can find the parameters:
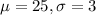
And for this case we select a sample size n =50. And since the sample size is higher than 30 we can use the central limit theorem and the distribution for the sample mean would be given by:
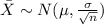
We want to find the following probability:
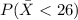
And we can use the z score formula given by:
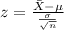
And replacing we got:
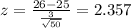
And we can find the probability using the normal distribution table and we got: