Answer:
The equation
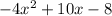 does not have any real zeroes.
does not have any real zeroes.
Explanation:
The given equation is
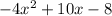 .
.
Let us compare it with standard quadratic equation
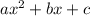
a = -4
b = 10
c = -8
The nature of zeroes is determined by Discriminant 'D'.
1. If D = 0, the quadratic equation has two equal real zeroes.
2. If D > 0, the quadratic equation has two unequal real zeroes.
3. If D < 0, the quadratic equation has two non-real or imaginary zeroes.
Formula for D is:
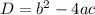
Putting the values of a, b and c to find D:
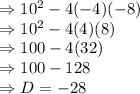
Here, D is negative so the zeroes of this quadratic equation are imaginary.
Hence, no real zeroes for the given equation
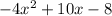 .
.