Answer: the speed at which products form
Step-by-step explanation:
Rate of a reaction is defined as the speed at which a chemical reaction proceeds. It is often expressed in terms of the concentration of a reactant that is consumed in a unit time or the concentration of a product that is formed in a unit of time.
For a general reaction :
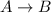
![Rate=-(d[A])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/40pb79s23568yf13kf8i8mxt3fv300re6p.png)
or
![Rate=+(d[B])/(dt)](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/middle-school/l5c9i3u8cb6sdt7xm60x1cqspwxl24btph.png)
where d[A] = change in concentration of reactant A
d[B] = change in concentration of product B
dt = time interval