Answer:
(i) t = 5s
(ii) x = 3.75*10^5 m
Step-by-step explanation:
(i) To calculate the time that the electron takes to reach twice the value of its initial velocity, you use the following formula:
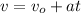 (1)
(1)
vo: initial velocity of the electron = 5*10^4 m/s
v: final velocity of the electron = 2vo = 1*10^5 m/s
a: acceleration of the electron = 1*10^4 m/s^2
You solve the equation (1) for t, and replace the values of the parameters:
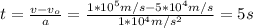
The electron takes 5s to reach twice its initial velocity.
(ii) The distance traveled by the electron in such a time is:
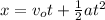 (2)
(2)
you replace the values of the parameters in the equation (2):
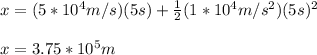
The distance traveled by the electron is 3.75*10^3m/s