Answer:
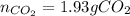
Step-by-step explanation:
Hello,
In this case, considering the given chemical reaction, we can use the molar mass of octane (114.23 g/mol) and the 2:16 molar ratio with carbon dioxide to compute the emitted moles of CO2 to the atmosphere via the following stoichiometric procedure:

Which also corresponds to the following mass:
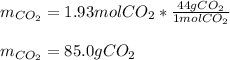
Best regards.