Answer:
97.8% of starting material
Step-by-step explanation:
In the reaction:
COBr₂(g) ⇄ CO(g) + Br₂(g)
Kp is defined as:
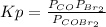 = 5.40
= 5.40
As initial pressure of COBr₂ is 0.123atm, the pressure at equilibrium of each is:
COBr₂(g) = 0.123atm - X
CO(g) = X
Br₂(g) = X
Where X is reaction coordinate, the amount of reactant that is converted to products
Replacing in Kp expression:
5.40 = X² / (0.123 - X)
0.6642 - 5.40X = X²
0 = X² + 5.40X - 0.6642
Solving for X:
X = -5.52 atm → False solution, there is no negative concentrations.
X = 0.1203 atm → Right solution
Thus, the fraction of starting material that is converted to products is:
0.1203atm / 0.123atm = 0.978 =
97.8% of starting material