Answer:
The frequencies are
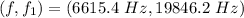
Step-by-step explanation:
From the question we are told that
The length of the ear canal is
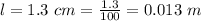
The speed of sound is assumed to be
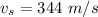
Now taking look at a typical ear canal we see that we assume it is a closed pipe
Now the fundamental harmonics for the pipe(ear canal) is mathematically represented as

substituting values
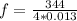

Also the the second harmonic for the pipe (ear canal) is mathematically represented as
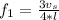
substituting values
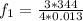
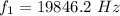
Given that sound would be loudest in the pipe at the frequency, it implies that the child will have an increased audible sensitivity at this frequencies