Answer:
This reaction isn't yet at an equilibrium. It must shift in the direction of the reactant (namely
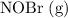 ) in order to reach an equilibrium.
) in order to reach an equilibrium.
For this mixture, the reaction quotient is
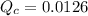 .
.
Step-by-step explanation:
A reversible reaction is at equilibrium if and only if its reaction quotient
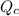 is equal to the equilibrium constant
is equal to the equilibrium constant
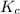 .
.
Start by calculating the equilibrium quotient
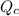 of this reaction. Given the reaction:
of this reaction. Given the reaction:
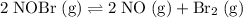 .
.
Let
![[\mathrm{NOBr\; (g)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4evr0xvlz1jkl6wp0ce1378vbp6xh8o4pt.png) ,
,
![[\mathrm{NO\; (g)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hlgyyaeqlf6mv67pbiwkov6ory1tpp0pj2.png) , and
, and
![[\mathrm{Br_2\; (g)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/i7m5w7m03qa7iun1ub59bkv0no3t87kxvm.png) denote the concentration of the three species. The formula for the reaction quotient of this system will be:
denote the concentration of the three species. The formula for the reaction quotient of this system will be:
![\displaystyle Q_c = \frac{[\mathrm{NO\; (g)}]^2 \cdot [\mathrm{Br_2\; (g)}]}{[\mathrm{NOBr\; (g)}]^2}](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/38dm84mtbrfjx4xki586tc33iayalzp3ra.png) .
.
(Note, that in this formula, both
![[\mathrm{NO\; (g)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/hlgyyaeqlf6mv67pbiwkov6ory1tpp0pj2.png) and
and
![[\mathrm{NOBr\; (g)}]](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/4evr0xvlz1jkl6wp0ce1378vbp6xh8o4pt.png) are raised to a power of two. That corresponds to the coefficients in the balanced reaction.)
are raised to a power of two. That corresponds to the coefficients in the balanced reaction.)
Calculate the reaction quotient given the concentration of each species:
![\displaystyle Q_c = \frac{[\mathrm{NO\; (g)}]^2 \cdot [\mathrm{Br_2\; (g)}]}{[\mathrm{NOBr\; (g)}]^2} \approx 1.26* 10^(-2) = 0.0126](https://img.qammunity.org/2021/formulas/chemistry/college/6nycxqjd72fmuq9mqbzxwy58ctydigsqny.png) .
.
(Note that the unit is ignored.)
Apparently,
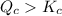 . Since
. Since
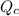 and
and
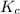 are not equal, this reaction is not at an equilibrium. If external factors like temperature stays the same,
are not equal, this reaction is not at an equilibrium. If external factors like temperature stays the same,
Keep in mind that
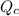 denotes a quotient. To reduce the value of a quotient, one may:
denotes a quotient. To reduce the value of a quotient, one may:
- reduce the value of the numerator,
- increase the value of the denominator, or
- both.
In
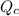 , that means reducing the concentration of the products while increasing the concentration of the reactants. In other words, the system needs to shift in the direction of the reactants before it could reach an equilibrium.
, that means reducing the concentration of the products while increasing the concentration of the reactants. In other words, the system needs to shift in the direction of the reactants before it could reach an equilibrium.